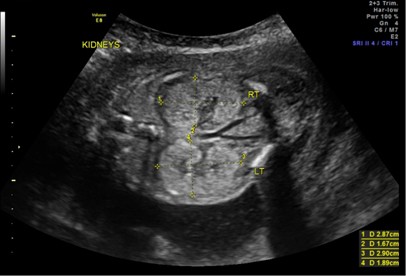
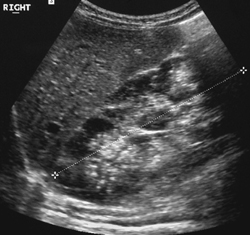
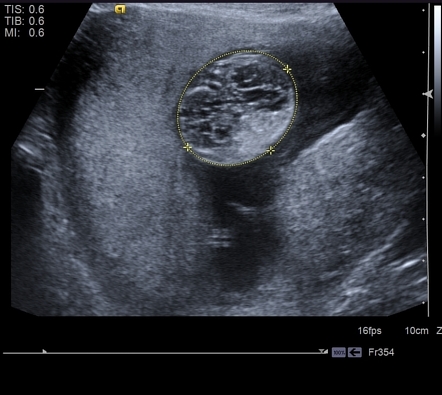
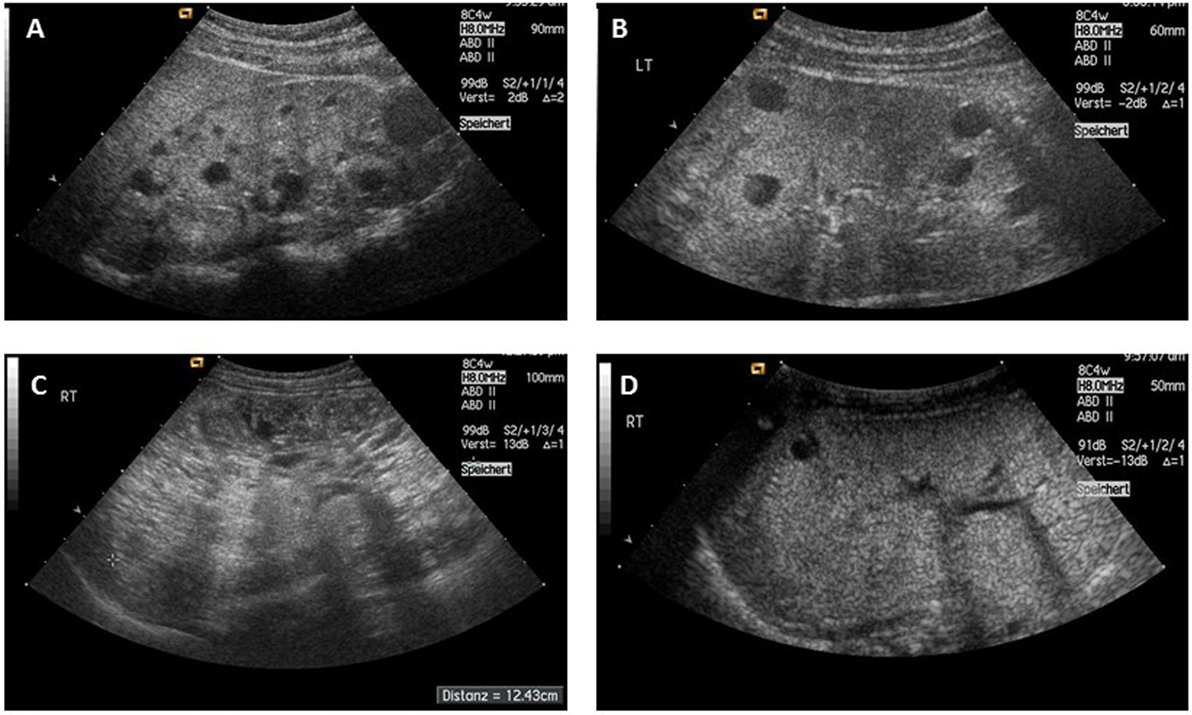
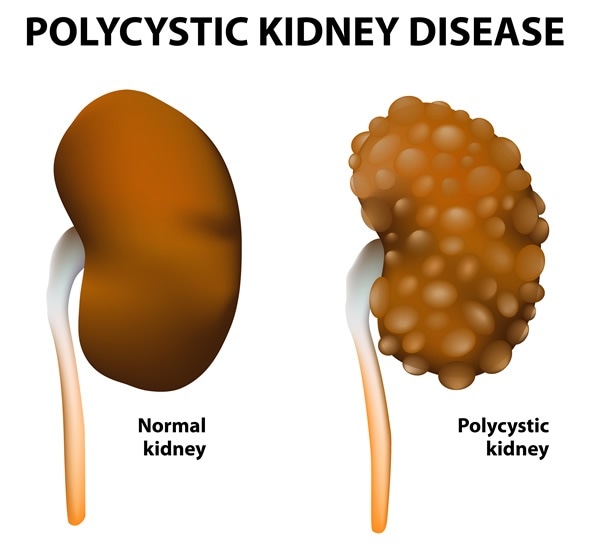
Polycystic Kidney Disease In Utero
Polycystic kidney disease in utero. Two pregnancies wereterminatedfollowingthedetectionof enlarged echogenic fetal kidneys with cysts. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is a genetic condition marked by the growth of numerous cysts fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. Sedman MDt Patricia A.
Manco-Johnson MD Gail R. D V Habif Jr. Polycystic kidneydisease PKD1 presentingin utero andprognosisforveryearly onsetdisease KDMacDermotAKSaggar-MalikDLEconomidesSJeffery Abstract Wedescribe four prenatal diagnoses in a family with autosomal dominant poly-cystic kidney disease.
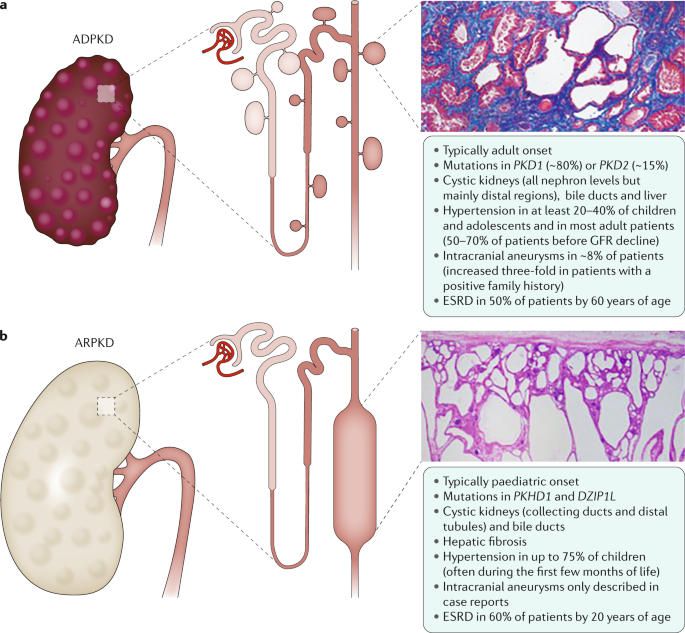
Cell presentation of PKD in second degree relatives 199477881-94. Infantile polycystic kidney disease. Polycystic kidney disease is a rare developmental anomaly inherited as autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive.
Urology Kidney and Bladder Diagnosis and Screening of Urologic Conditions Kidney Procedures What is polycystic kidney disease. Polycystic kidney disease Concept Id. We report five cases and review eight cases from the literature of ADPKD diagnosed in the fetus or the young infant by sonographic evaluation and a positive family history.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is one of most common inherited renal diseases. The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive review of genetics prenatal diagnosis and prognosis in very early onset autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. While the majority of patients are diagnosed in adulthood diagnosis in earlier ages has increased due to development of ultrasonography.
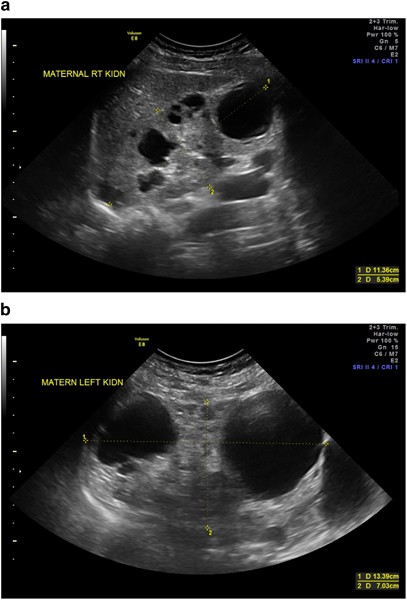
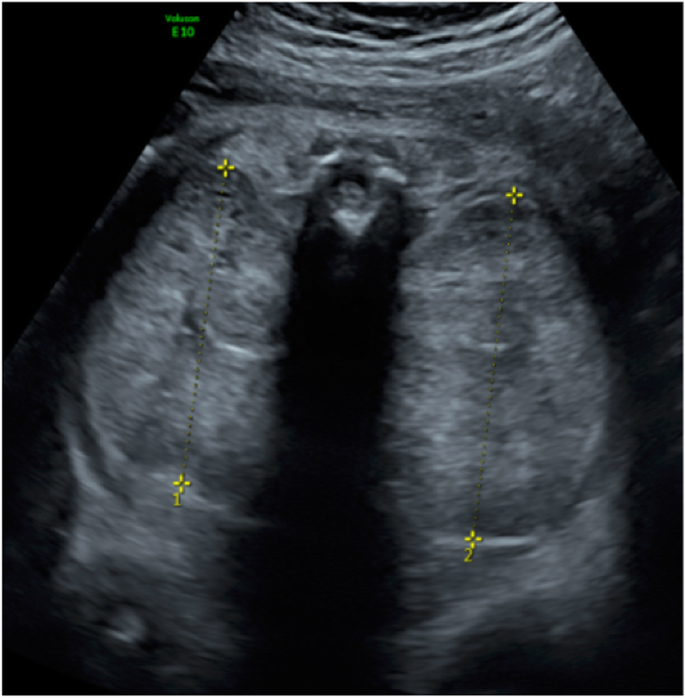
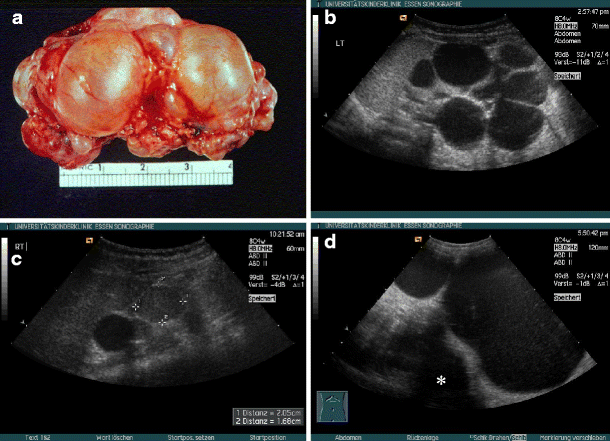
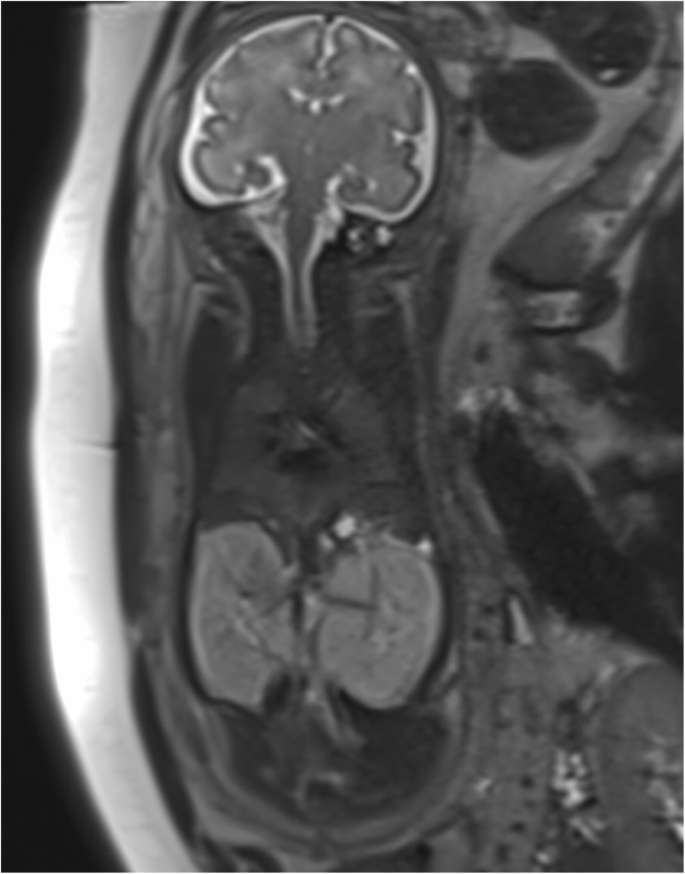
In utero diagnosis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease 182 Acta Obstet Ginecol Port 2020143179-183 ing to progressive bilateral formation of cortical and medullary renal cysts 6. The infantile and juvenile types result in chronic renal failure hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension. D V Habif Jr W E Berdon and M N Yeh 1982-02-01 000000 Kidney Sonographic A family had three consecutive pregnancies.
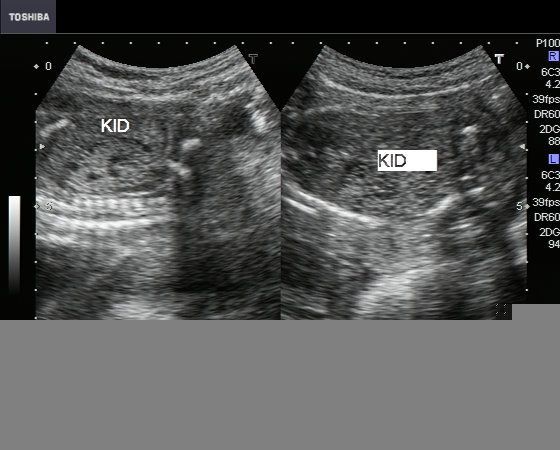
In utero sonographic diagnosis. The cysts become larger and the kidneys enlarge along with them.
PKD1 located on chromosome 16 16p133 1 which is responsible for 85 of the cases and PKD2 on chromosome 4 4q1323 2 3 responsible for 15.
The autosomal dominant trait is associated with abnormalities on the short arm of chromosome 16. Polycystic kidney disease is a rare developmental anomaly inherited as autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. D V Habif Jr W E Berdon M N Yeh. Infantile polycystic kidney disease. Longitudinal follow up of 24 children in two studies showed that 67 of survivors developed hypertension of whom three had end stage renal failure at a mean age of 3 years. The autosomal dominant trait is associated with abnormalities on the short arm of chromosome 16. Polycystic kidney disease Concept Id. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is a genetic condition marked by the growth of numerous cysts fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. D V Habif Jr.
C0022680 A usually autosomal dominant and less frequently autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by the presence of numerous cysts in the kidneys leading to end-stage renal failure. Of 83 reported cases of ADPKD presenting in utero excluding termination of pregnancy or in the first few months of life 43 died before 1 year. Two genes have been identified to date. Many cases survive into their teens and require renal transplant. In utero sonographic diagnosis. The cysts become larger and the kidneys enlarge along with them. It is included in the differential diagnosis of cystic diseases of the kidney.



























Post a Comment for "Polycystic Kidney Disease In Utero"